Navigating Corporate Waters: Tips for Surviving as a New Finance Director

Navigating Corporate Waters: Tips for Surviving as a New Finance Director
Introduction
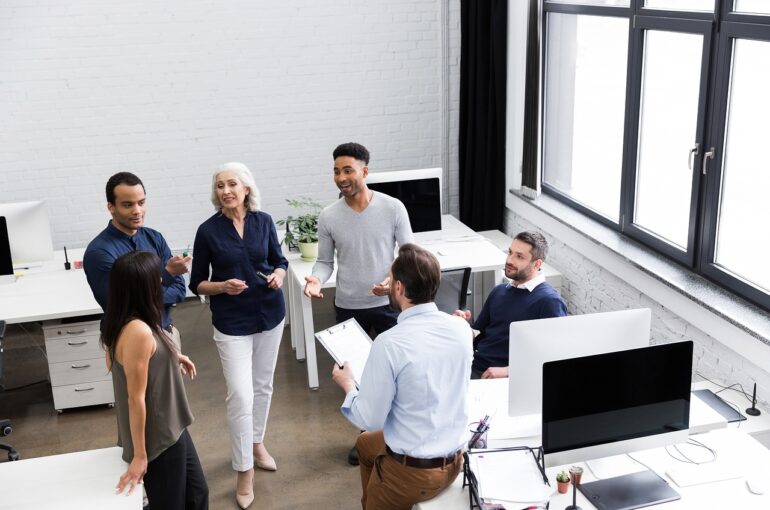
Stepping into the role of a Finance Director for the first time can be both exhilarating and daunting. The corporate landscape is a complex and dynamic environment, where financial acumen must be paired with strategic vision and leadership skills. As a new Finance Director, you are not only responsible for managing the financial health of the organization but also for steering it towards sustainable growth and profitability. This article aims to provide you with essential tips and insights to help you navigate these corporate waters effectively. From understanding your new responsibilities to building a strong team and fostering strategic partnerships, we will explore the key areas that will set you up for success in your new role.
Understanding Your Role and Responsibilities
Defining the Scope of Your Position
As a new Finance Director, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the scope of your position. This involves knowing the specific duties and expectations that come with your role. Typically, a Finance Director is responsible for overseeing the financial health of the organization, which includes managing budgets, financial planning, and financial reporting. It is essential to familiarize yourself with the company’s financial policies, procedures, and systems to effectively manage these responsibilities.
Key Responsibilities
Financial Planning and Analysis
One of the primary responsibilities of a Finance Director is to lead the financial planning and analysis (FP&A) efforts. This includes developing long-term financial strategies, creating annual budgets, and forecasting future financial performance. You will need to analyze financial data to identify trends, variances, and opportunities for improvement. This analysis will inform strategic decision-making and help the organization achieve its financial goals.
Budget Management
Effective budget management is a critical aspect of your role. You will be responsible for creating, monitoring, and adjusting the company’s budget to ensure financial stability and growth. This involves working closely with department heads to understand their financial needs and constraints, as well as ensuring that expenditures align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Financial Reporting
Accurate and timely financial reporting is essential for maintaining transparency and accountability within the organization. As a Finance Director, you will oversee the preparation of financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. You will also be responsible for ensuring compliance with relevant accounting standards and regulations.
Risk Management
Identifying and mitigating financial risks is another key responsibility. This involves assessing potential risks related to investments, operations, and external factors, and developing strategies to minimize their impact. You will need to stay informed about changes in the economic environment and industry trends that could affect the organization’s financial health.
Leadership and Team Management
Building and Leading a Finance Team
As a Finance Director, you will lead a team of finance professionals. This includes recruiting, training, and developing team members to ensure they have the skills and knowledge needed to perform their roles effectively. You will also need to foster a collaborative and supportive work environment that encourages continuous improvement and innovation.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Collaboration with other departments is essential for achieving the organization’s financial objectives. You will need to work closely with executives, managers, and other stakeholders to align financial strategies with overall business goals. This may involve participating in strategic planning sessions, providing financial insights, and supporting key initiatives.
Compliance and Governance
Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring compliance with financial regulations and standards is a critical aspect of your role. This includes staying up-to-date with changes in laws and regulations that affect the organization’s financial practices. You will need to implement and maintain internal controls to prevent fraud and ensure the accuracy of financial reporting.
Corporate Governance
Strong corporate governance practices are essential for maintaining the trust of stakeholders and ensuring the long-term success of the organization. As a Finance Director, you will play a key role in promoting ethical behavior, transparency, and accountability within the organization. This may involve working with the board of directors, audit committees, and other governance bodies to establish and enforce governance policies and procedures.
Strategic Financial Leadership
Driving Financial Strategy
As a Finance Director, you will be responsible for driving the organization’s financial strategy. This involves setting financial goals, developing plans to achieve them, and monitoring progress. You will need to provide strategic financial guidance to the executive team and help shape the overall direction of the organization.
Supporting Business Growth
Supporting business growth is a key aspect of your role. This may involve identifying and evaluating new business opportunities, securing financing, and managing mergers and acquisitions. You will need to balance the pursuit of growth with the need to maintain financial stability and manage risks effectively.
Building Strong Relationships with Key Stakeholders
Identifying Key Stakeholders
Understanding who your key stakeholders are is the first step in building strong relationships. Key stakeholders can include:
- Internal Stakeholders: These are individuals within the organization such as the CEO, CFO, department heads, and team members. They are directly impacted by your financial decisions and strategies.
- External Stakeholders: These include investors, shareholders, clients, suppliers, and regulatory bodies. Their interests and expectations can significantly influence your role and responsibilities.
Understanding Stakeholder Needs and Expectations
To build strong relationships, it is crucial to understand what each stakeholder values and expects from you. This involves:
- Conducting Stakeholder Analysis: Identify the interests, influence, and expectations of each stakeholder. This can be done through surveys, interviews, and reviewing past interactions.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Align your financial strategies and goals with the needs and expectations of your stakeholders. This ensures that your actions are relevant and beneficial to them.
Effective Communication
Clear and consistent communication is key to maintaining strong relationships with stakeholders. This can be achieved through:
- Regular Updates: Provide timely and transparent updates on financial performance, strategic initiatives, and any changes that may impact stakeholders.
- Tailored Communication: Customize your communication style and content to suit the preferences and understanding levels of different stakeholders. For example, detailed financial reports for the CFO and high-level summaries for the CEO.
- Active Listening: Engage in two-way communication by actively listening to stakeholder feedback and concerns. This helps in building trust and addressing issues proactively.
Building Trust and Credibility
Trust and credibility are the foundation of strong stakeholder relationships. To build these, focus on:
- Consistency and Reliability: Ensure that your actions and decisions are consistent and reliable. This builds confidence in your ability to manage the organization’s finances effectively.
- Transparency: Be open and honest about financial challenges and opportunities. Transparency fosters trust and allows stakeholders to make informed decisions.
- Delivering on Promises: Follow through on commitments and deliver results as promised. This demonstrates your reliability and strengthens your credibility.
Collaboration and Engagement
Engaging stakeholders in the decision-making process can enhance relationships and drive better outcomes. This involves:
- Involving Stakeholders in Planning: Include key stakeholders in financial planning and strategy sessions. Their input can provide valuable insights and foster a sense of ownership.
- Creating Collaborative Opportunities: Facilitate opportunities for stakeholders to collaborate on projects and initiatives. This can lead to innovative solutions and stronger partnerships.
- Recognizing and Valuing Contributions: Acknowledge and appreciate the contributions of stakeholders. This reinforces their importance and encourages continued engagement.
Managing Conflicts and Challenges
Conflicts and challenges are inevitable in any organization. Effectively managing these situations is crucial for maintaining strong relationships. This can be done by:
- Addressing Issues Promptly: Tackle conflicts and challenges head-on and in a timely manner. Delaying resolution can exacerbate issues and damage relationships.
- Finding Common Ground: Focus on common goals and interests to find mutually beneficial solutions. This helps in resolving conflicts amicably.
- Maintaining Professionalism: Handle conflicts with professionalism and respect. This sets a positive tone and demonstrates your commitment to maintaining strong relationships.
Mastering Financial Reporting and Analysis
Understanding Financial Statements
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It includes assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. As a finance director, you must understand how to read and interpret each section to assess the company’s financial health.
Income Statement
The income statement, or profit and loss statement, shows the company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a period. Mastering this statement helps you evaluate operational efficiency and profitability.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement outlines the inflows and outflows of cash within the business. It is crucial for understanding liquidity and ensuring the company can meet its short-term obligations.
Key Financial Ratios
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios, such as the current ratio and quick ratio, measure the company’s ability to meet short-term liabilities. These ratios are essential for assessing financial stability.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios, including gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin, help evaluate the company’s ability to generate profit relative to sales, assets, and equity.
Leverage Ratios
Leverage ratios, like the debt-to-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio, assess the level of debt in the company’s capital structure and its ability to meet financial obligations.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios, such as inventory turnover and accounts receivable turnover, measure how effectively the company uses its assets to generate revenue.
Financial Analysis Techniques
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis involves comparing financial data over multiple periods to identify patterns and trends. This technique helps in forecasting future performance and making informed decisions.
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis, or benchmarking, involves comparing the company’s financial metrics with industry standards or competitors. This helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting financial ratios to assess various aspects of the company’s performance, such as liquidity, profitability, and solvency.
Utilizing Financial Software and Tools
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP systems integrate various business processes, including financial reporting and analysis. Familiarity with ERP systems can streamline data collection and reporting.
Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
BI tools, such as Tableau and Power BI, help visualize financial data and generate insightful reports. These tools enhance decision-making by providing real-time data analysis.
Financial Modeling Software
Financial modeling software, like Excel and specialized tools, assists in creating detailed financial models for budgeting, forecasting, and scenario analysis.
Communicating Financial Insights
Preparing Clear and Concise Reports
Effective financial reporting involves presenting data in a clear, concise, and understandable manner. Use visual aids, such as charts and graphs, to enhance comprehension.
Tailoring Communication to the Audience
Different stakeholders have varying levels of financial expertise. Tailor your communication to meet the needs of your audience, whether they are board members, investors, or department heads.
Highlighting Key Metrics and Trends
Focus on key metrics and trends that impact the business. Highlighting these areas helps stakeholders understand the company’s performance and make informed decisions.
Implementing Effective Financial Controls
Establish Clear Policies and Procedures
Document Financial Processes
Creating detailed documentation for all financial processes is crucial. This includes everything from budgeting and forecasting to expense management and financial reporting. Clear documentation ensures that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
Standardize Procedures
Standardizing procedures across the organization helps maintain consistency and accuracy. This can involve using standardized forms, templates, and checklists for financial transactions and reporting. Standardization also makes it easier to train new employees and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Segregation of Duties
Divide Responsibilities
Segregation of duties is a fundamental principle of internal control. By dividing responsibilities among different employees, you reduce the risk of fraud and errors. For example, the person who authorizes payments should not be the same person who processes them.
Implement Checks and Balances
Implementing checks and balances involves having multiple layers of review and approval for financial transactions. This can include requiring multiple signatures for large expenditures or having a separate team review financial reports before they are finalized.
Regular Audits and Reviews
Internal Audits
Conducting regular internal audits helps identify weaknesses in financial controls and ensures compliance with policies and procedures. Internal audits can be performed by an in-house team or an external firm, depending on the size and complexity of the organization.
External Audits
External audits provide an independent assessment of the organization’s financial health and control environment. They can help identify areas for improvement and provide assurance to stakeholders that the financial statements are accurate and reliable.
Implement Technology Solutions
Financial Management Software
Investing in financial management software can streamline processes and improve accuracy. These systems can automate tasks such as invoicing, payroll, and financial reporting, reducing the risk of human error and freeing up time for more strategic activities.
Data Analytics
Using data analytics tools can help identify trends and anomalies in financial data. This can provide valuable insights for decision-making and help detect potential fraud or errors early.
Training and Education
Ongoing Training Programs
Providing ongoing training for employees ensures they are up-to-date with the latest financial practices and regulatory requirements. Training programs can cover topics such as fraud prevention, financial reporting standards, and the use of financial software.
Encourage a Culture of Compliance
Encouraging a culture of compliance involves promoting ethical behavior and accountability throughout the organization. This can be achieved through regular communication, setting a strong example at the leadership level, and recognizing employees who demonstrate a commitment to compliance.
Monitoring and Reporting
Real-Time Monitoring
Implementing real-time monitoring systems allows for continuous oversight of financial transactions. This can help detect and address issues as they arise, rather than waiting for periodic reviews or audits.
Regular Reporting
Regular financial reporting provides transparency and keeps stakeholders informed about the organization’s financial health. This can include monthly financial statements, budget vs. actual reports, and key performance indicators (KPIs). Regular reporting also helps identify trends and areas for improvement.
Navigating Corporate Politics
Understanding the Landscape
Identifying Key Players
Recognizing who holds power and influence within the organization is crucial. This includes not only those in senior management but also informal leaders who may not have official titles but wield significant influence. Understanding the dynamics between these key players can help you navigate the corporate environment more effectively.
Mapping Relationships
Create a mental or physical map of relationships within the company. This includes understanding alliances, rivalries, and historical conflicts. Knowing who is aligned with whom can provide insights into potential support or opposition you might face.
Building Strategic Alliances
Networking
Developing a strong network within the organization is essential. Attend company events, join committees, and engage in informal gatherings. Building relationships across different departments can provide support and open doors to new opportunities.
Finding Mentors and Sponsors
Identify potential mentors and sponsors who can provide guidance and advocate for you. Mentors offer advice and share their experiences, while sponsors actively promote your career advancement within the organization.
Communication Skills
Active Listening
Effective communication starts with active listening. Pay attention to what others are saying, ask clarifying questions, and show empathy. This helps build trust and demonstrates that you value others’ perspectives.
Clear and Concise Messaging
When communicating, be clear and concise. Avoid jargon and ensure your message is easily understood. Tailor your communication style to your audience, whether it’s senior management, peers, or subordinates.
Managing Conflicts
Addressing Issues Early
Address conflicts early before they escalate. Approach the situation calmly and objectively, focusing on the issue rather than personal differences. Seek to understand the other party’s perspective and work towards a mutually beneficial resolution.
Seeking Mediation
If conflicts cannot be resolved directly, seek mediation from a neutral third party. This could be a human resources representative or an external mediator. Mediation can help facilitate a fair and unbiased resolution.
Ethical Considerations
Maintaining Integrity
Always maintain your integrity, even when navigating complex political situations. Uphold ethical standards and avoid compromising your values for short-term gains. Your reputation is one of your most valuable assets.
Transparency
Be transparent in your actions and decisions. Transparency builds trust and credibility, which are essential for long-term success. When making decisions, clearly communicate the rationale and be open to feedback.
Leveraging Emotional Intelligence
Self-Awareness
Develop self-awareness to understand your emotions and how they impact your behavior. Recognize your strengths and weaknesses, and seek feedback to improve continuously.
Empathy
Empathy is crucial for understanding others’ emotions and perspectives. Practice empathy by actively listening, showing compassion, and considering how your actions affect others. This can help build stronger relationships and foster a positive work environment.
Leading and Developing Your Finance Team
Establishing Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Defining clear roles and responsibilities is crucial for the smooth functioning of your finance team. Each team member should have a well-defined job description that outlines their specific duties, reporting lines, and performance expectations. This clarity helps in avoiding overlaps and ensures accountability. Regularly review and update these roles to adapt to changing business needs and individual career growth.
Fostering a Collaborative Environment
Creating a collaborative environment is essential for the success of your finance team. Encourage open communication and the sharing of ideas. Implement regular team meetings and brainstorming sessions where everyone can contribute. Use collaborative tools and platforms to facilitate seamless interaction, even if your team is working remotely. A culture of collaboration not only enhances productivity but also fosters innovation and problem-solving.
Providing Continuous Training and Development
Investing in the continuous training and development of your team members is vital. Offer opportunities for professional development through workshops, seminars, and online courses. Encourage team members to pursue relevant certifications and advanced degrees. Create a mentorship program where experienced team members can guide and support newer or less experienced colleagues. Continuous learning helps in keeping the team updated with the latest industry trends and best practices.
Setting Performance Goals and Metrics
Setting clear performance goals and metrics is essential for tracking the progress and effectiveness of your finance team. Develop SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals that align with the overall objectives of the organization. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure individual and team performance. Regularly review these metrics and provide constructive feedback to help team members improve and stay on track.
Encouraging Innovation and Process Improvement
Encouraging innovation and process improvement within your finance team can lead to significant efficiencies and cost savings. Create an environment where team members feel comfortable suggesting new ideas and approaches. Implement a structured process for evaluating and implementing these suggestions. Recognize and reward innovative thinking and successful process improvements to motivate the team further.
Building a Strong Team Culture
Building a strong team culture is fundamental to the long-term success of your finance team. Promote values such as integrity, accountability, and mutual respect. Organize team-building activities and social events to strengthen relationships and foster a sense of belonging. Celebrate achievements and milestones to boost morale and create a positive work environment. A strong team culture enhances employee satisfaction and retention.
Leveraging Technology and Tools
Leveraging the right technology and tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your finance team. Invest in modern financial software and tools that streamline processes such as budgeting, forecasting, and reporting. Ensure that your team is well-trained in using these tools to maximize their benefits. Stay updated with the latest technological advancements and be open to adopting new solutions that can drive better results.
Promoting Work-Life Balance
Promoting work-life balance is essential for maintaining the well-being and productivity of your finance team. Encourage flexible working hours and remote work options where feasible. Provide resources and support for managing stress and maintaining mental health. Recognize the importance of personal time and discourage a culture of overwork. A healthy work-life balance leads to happier, more engaged, and more productive team members.
Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Importance of Continuous Learning
In the fast-paced world of finance, staying updated with the latest trends, regulations, and technologies is crucial. Continuous learning ensures that you remain relevant and can make informed decisions that benefit your organization. It also enhances your ability to adapt to changes, whether they are market-driven or regulatory.
Professional Certifications
Obtaining professional certifications such as CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst), CPA (Certified Public Accountant), or CMA (Certified Management Accountant) can significantly boost your credibility and expertise. These certifications not only validate your skills but also provide you with a structured learning path that covers essential aspects of finance and accounting.
Attending Workshops and Seminars
Workshops and seminars offer opportunities to learn from industry experts and peers. These events often cover the latest trends, tools, and best practices in finance. They also provide a platform for networking, which can be invaluable for career growth and staying informed about industry developments.
Online Courses and Webinars
Online courses and webinars offer flexibility and convenience, allowing you to learn at your own pace. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and LinkedIn Learning offer a wide range of courses tailored to finance professionals. Webinars, often hosted by industry leaders, provide insights into specific topics and emerging trends.
Reading Industry Publications
Staying updated with industry publications such as The Wall Street Journal, Financial Times, and industry-specific journals can provide you with the latest news, trends, and in-depth analyses. Subscribing to newsletters and following thought leaders on social media can also keep you informed.
Networking and Mentorship
Building a strong professional network can open doors to new opportunities and provide support when navigating challenges. Joining professional organizations, attending industry events, and participating in online forums can help you connect with like-minded professionals. Seeking mentorship from experienced finance directors can provide valuable guidance and insights.
Internal Training Programs
Many organizations offer internal training programs designed to enhance the skills of their employees. These programs can range from technical training on new software to leadership development courses. Taking advantage of these opportunities can help you stay ahead and contribute more effectively to your organization.
Staying Technologically Savvy
The finance industry is increasingly reliant on technology, from data analytics to blockchain. Staying technologically savvy involves not only understanding the tools and software used in your organization but also keeping an eye on emerging technologies that could impact the industry. Enrolling in courses on data analytics, cybersecurity, and financial technologies can be beneficial.
Peer Learning and Collaboration
Learning from your peers can be incredibly valuable. Engaging in collaborative projects, participating in cross-functional teams, and sharing knowledge within your organization can enhance your learning experience. Peer learning fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Setting Personal Learning Goals
Setting personal learning goals can help you stay focused and motivated. Whether it’s mastering a new software, understanding a complex financial model, or improving your leadership skills, having clear objectives can guide your learning journey. Regularly reviewing and updating these goals ensures that you are continually progressing.
Leveraging Feedback
Feedback from colleagues, supervisors, and mentors can provide insights into areas where you can improve. Actively seeking and acting on feedback helps you refine your skills and grow professionally. It also demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement, which is highly valued in any organization.
Related posts:
Strategic Financial Leadership: Choosing Between a CFO and a Finance Director
Flexible Financial Leadership Models: Unlocking Growth with Part-Time CFOs and FDs
Exit-Ready in 12 Months: The FD’s Roadmap to Maximise Valuation
Maximizing Business Growth: The Strategic Advantages of Hiring a Part-Time Finance Director

Adrian Lawrence FCA with over 25 years of experience as a finance leader and a Chartered Accountant, BSc graduate from Queen Mary College, University of London.
I help my clients achieve their growth and success goals by delivering value and results in areas such as Financial Modelling, Finance Raising, M&A, Due Diligence, cash flow management, and reporting. I am passionate about supporting SMEs and entrepreneurs with reliable and professional Chief Financial Officer or Finance Director services.